Gestational Diabetes
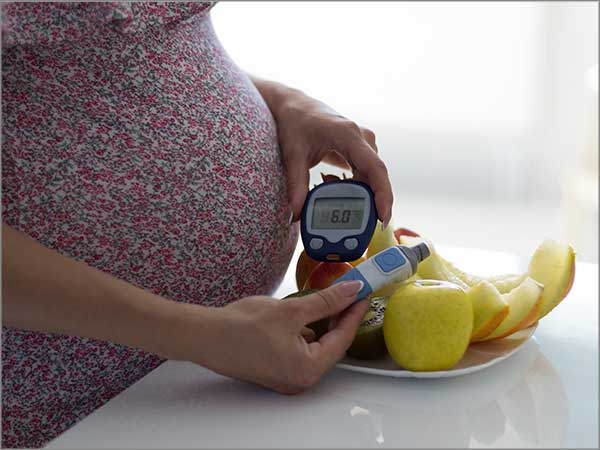
High blood sugar that develops during pregnancy is known as Gestational Diabetes. It usually disappears after the delivery of the child. While it can occur at any stage of pregnancy; it is more common in the second half.
Gestational diabetes can cause problems during and after birth. But if it’s detected and well managed the risk can be reduced.
Risk factors
While any woman can develop gestational diabetes, some women are at greater risk. Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Age above 25
- Personal or family health history
- If you’ve gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy
- If you had an unexplained stillbirth or delivered a baby who weighed more than 4.1 kilograms.
- Excess weight with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes is mostly detected when your blood sugar level is tested.
If the blood sugar level gets too high some women may develop symptoms such as:
- Increased thirst
- Needing to urinate more often than usual
- A dry mouth
- Tiredness
Prevention
When it comes to preventing gestational diabetes there are no guarantees. However, it is better to adopt more healthy habits before pregnancy.
Eat healthy food. Include food that is high in fiber and low in fat and calories like fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Be active. To help protect you from developing gestational diabetes, exercise before and during pregnancy.
Lose excess pounds before pregnancy. But don’t try to lose weight during pregnancy. Doctors don’t recommend that.
Diet
You can control your blood sugar levels by making changes to your diet.
We will refer to a dietitian, who can give you advice about your diet, and even help you plan your meals.
You may be advised to:
- Eat regularly and avoid skipping meals
- Eat low Glycaemic Index (GI) foods such as brown rice, whole-wheat pasta, all-bran cereals, granary bread, beans, pulses, muesli, lentils, and porridge. They release sugar slowly.
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits
- Avoid sugary foods but there is no need to follow a completely sugar-free diet. Eat healthier alternatives like nuts, fruits and seeds and avoid biscuits and cakes.
- Avoid sugary drinks and opt for "no added sugar" drinks.
- Include lean sources of protein in your diet, such as fish
Medication
If your blood sugar level is not under control a week or two after changing your diet and exercising regularly you may be prescribed certain medications.
As your pregnancy progresses your blood sugar level can increase, so you may need to take medication later in pregnancy even if your blood glucose levels are well controlled at first.
After delivery, these medications will be stopped.
Monitoring your pregnancy
You’ll be offered extra antenatal appointments as gestational diabetes can increase the risk of your baby developing problems.
Appointments include:
- To check your baby for abnormalities an ultrasound scan at around weeks 18-20 of your pregnancy
- Ultrasound scans at weeks 28, 32 and 36 to monitor your baby’s growth, and regular checks from week 38.