Dyslipidemia
The fatty substances present in blood like cholesterol and triglycerides are known as blood lipids. When blood lipid levels are too high in a person, it is defined as Dyslipidemia.
By eating a balanced diet and making lifestyle changes many people achieve healthy levels of blood lipids. However, to prevent additional health problems some require medication.
The term Dyslipidemia describes a wide range of conditions. The most common forms of dyslipidemia are:
- Bad cholesterol or high levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
- Good cholesterol, or low levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
- High triglyceride levels
- High total cholesterol levels
While LDL cholesterol can cause plaques to form in the blood vessels, HDL cholesterol can help remove LDL from the blood.
When calories are not burned right away and are stored in fat cells it leads to increased cholesterol.
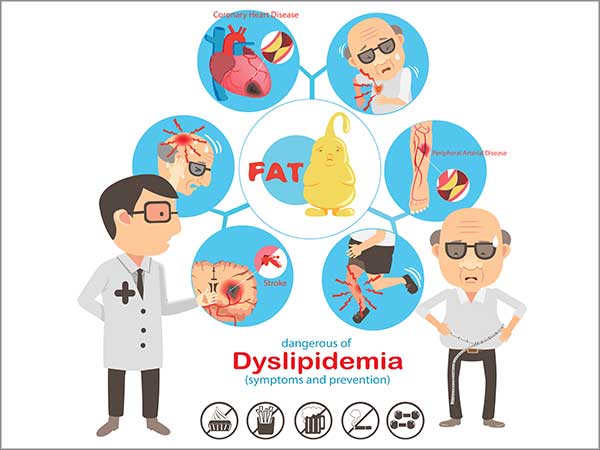
Symptoms
Most people are unaware that they have dyslipidemia unless it is severe. During a routine blood test dyslipidemia is usually diagnosed by a doctor.
Untreated dyslipidemia can lead to other conditions, including peripheral artery disease (PAD) and coronary artery disease (CAD), which can cause heart attacks and strokes.
Common symptoms of these conditions include:
- Leg pain
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Tightness, pain, and pressure in the jaw, neck, shoulders, and back
- Heartburn and indigestion
- Daytime exhaustion and sleep problems
- Dizziness
- Heart palpitations
- Cold sweats
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swelling in the ankles, legs, stomach, feet, and veins of the neck
- Fainting
With activity or stress, these symptoms may get worse.
If you have any of these symptoms along with chest pain, consult a doctor
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the chances of developing dyslipidemia and related conditions. They are:
- Obesity
- A sedentary lifestyle
- A lack of regular physical exercise
- Alcohol use
- Tobacco use
- Use of illegal or illicit drugs
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Chronic kidney or liver conditions
- Digestive conditions
- Older age
- A diet rich in saturated fats
- A parent or grandparent with dyslipidemia
- After menopause women tend to experience higher LDL levels
Treatment
A doctor will usually focus on lowering a person’s triglycerides and LDL. However, depending on the underlying cause of dyslipidemia and how severe it is, treatments can vary.
For people with very high total cholesterol levels doctors may prescribe one or more lipid-modifying medications.
Natural treatments include:
- Reducing the consumption of unhealthy fats, like red meats, refined carbohydrates, full-fat dairy products, chocolate, chips, and fried foods
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Avoiding or reducing alcohol consumption
- Quitting smoking and tobacco use
- Avoiding sitting for long periods of time
- Increasing consumption of healthy polyunsaturated fats, such as those found in seeds, nuts, fish, legumes, whole grains, and olive oil
- Taking omega-3 supplements
- Eating plenty of whole fruits, vegetables, and whole grains loaded with dietary fiber
- Drinking plenty of water